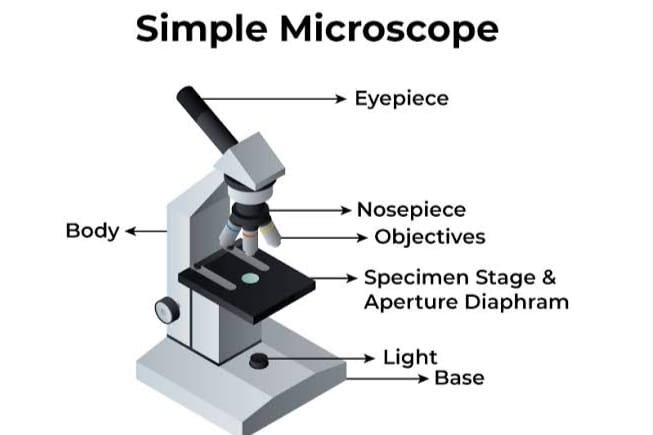
- Introduction of compound microscope
- Principle of compound microscope
- Parts of compound microscope
- Working of the microscope
- Use of microscope
- Care and maintenance
Introduction of compound microscope:-
The compound microscope consists of more than one glass lens in combination. The major lenses are the eye piece, the objective lenses and the condenser lenses. Each of these components is in turn made up of combinations of lenses, which is necessary to produce magnified images with reduced artifacts and aberrations. For example chromatic aberration occurs when different wavelength of light are separated and pass through a lens at different angles. This results in rainbow colours around the edge of the object in the image. A compound microscope consists of the following parts;
Principle of compound microscope :-
Produce dark image against a bright background for light transmission and image creation.
Parts of compound microscope:-
- Optical part
- mechanical part
Optical part of compound microscope:-
- Mirror[Plane & concave]
- Objective lens
- eye piece
Mirror[Plane & concave]:-
The mirror reflects rays from the light source on to the object. One side has a concave surface and the other a plane mirror. In the absence of a condenser the concave surface of the mirror should be used since concave surface forms a low power condenser. In the presence of a condenser the plain surface of the mirror should be used.
it is attached to the lower part of the arm . it is used to the reflecting light rays in to the microscope
Objective lens
- he magnifying power of each objective is shown by a figure engraved on the sleeve of the lens as follows:
| magnifying power | magnification |
| 10x | 10 times |
| 40x | 40 times |
| 100x | 100 times |
- The third objective is called oil immersion.
- It is marked with a red ring. It must be used with immersion oil.
- The numerical aperture (NA) is also engraved on the sleeve, next to the magnification
- The recommended length between the objective and the eyepiece is usually 160 mm.
- The recommended thickness of the coverslip = 0.17 mm.
- The screw threads of all the objectives are standard so that the objectives in the revolving nosepiece are interchangeable.
- The distance between the front lens of the objective and the object slide (when the image is in focus)
| objectives | working distance |
| 10x | 5.0-6.0 mm |
| 40x | 0.5-1.0 mm |
| 100x | 1.5-0.20mm |
Eye piece:-
- It is made up of two lenses, upper eye lens and lower field lens. The magnifying power of the eyepiece is marked on it and magnification of the image produced is as shown below:
| magnifying power | magnification |
| 4x | 4 times |
| 6x | 6 times |
| 10x | 10 times |
Mechanical part Of compound microscope
Following part:-
- Base
- pillar
- inclination joint
- Arm
- Stage
- Clips
- Diaphragm
- Body tube
- Revolving Nose base
- course adjustment screw
- fine adjustment tube
Base:-
- It is usually horse shoes shape structure.
- It provide a stable support for the microscope.
pillar:-
- It is usually small vertical projection from the base.
Inclination joint:-
- At this joint the arm is attached to the pillar ,the microscope can be fixed at the joint.
Arm:-
it is usually curved and it is used for handling the instrument.
Stage:-
- It is used for keeping the slide and magnifying object image.
- hole present in the Centre for the light rays are passed.
Clips:-
- There are two clips attached to the stage.
- it is used for holding the slide in position.
Diaphragm:-
- It is attached to the base of a stage.
- it regulates the amount of light.
- it has two type 1. disc 2.iris
Body tube:-
- It is a tubular hollow part attached to the upper part of the arm.
- it can move up and down with the help of a Screw.
Revolving Nose base:-
- It is a circular hollow tube metallic structure below the buddy tube.
- three different objective lenses can be fitted.
course adjustment screw:-
- It is bigger and can move the body up and down for focusing.
fine adjustment tube:-
- It is smaller in size for very slow movement needed for fine and sharp movement.
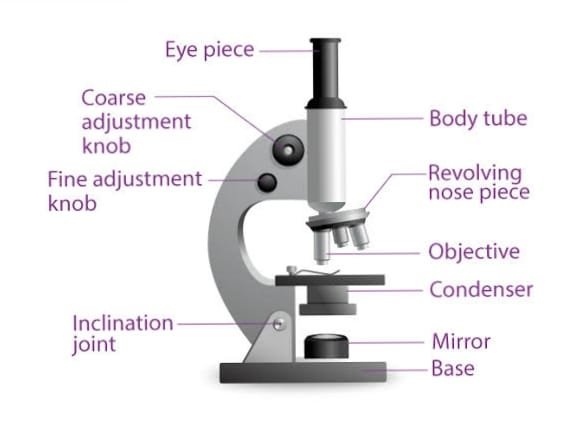
Working of the microscope
- Use of low power objective (X5 or X10)
- Adjust the condenser to the lowest position.
- Lower the objective until it is just above the slide preparation.
- Raise the objective by using the coarse adjustment screw, until a clear image is seen in the eyepiece.
- Use of high power objective (X40)
- Adjust the condenser about half way down.
- When the object is already adjusted on a low power objective, by using coarse adjustment raise the objective very slowly until a blurred image appears on the field.
- Bring the image into focus using the fine adjustment. Raise the condenser for sufficient illumination.
- Use of oil immersion objective (X100)
- Adjust the condenser to the uppermost position. Open the iris diaphragm fully.
- Place a tiny drop of immersion oil on the dry stained preparation of the slide
- Lower the objective until it is in contact with the oil.
Use of microscope:-
- medical laboratory
- Botanical Field.
- Biological Field.
- Crime Investigation.
- Educational Field.
- Medical Field.
Care and maintenance of compound microscope
Requirement
- Clean fine piece of linen cloth
- White absorbent tissue paper
- Xylene
- Soft cloth
- Petroleum jelly
- Plastic cover
- A fine paint brush
- Cleaning the objectives
- Dry objectives
- Wipe the objectives by using a soft cloth by moving the cloth across (and not circularly).
- Oil immersion objectives
- a) Remove the oil with an absorbent paper or a dry piece of cloth.
- b) Moisten the cloth with xylene and wipe the lens carefully.
- c) Wipe again with dry piece of cloth.
- Cleaning the eyepieces
- Clean the upper surface of the eyepiece (eye contact) with a soft cloth (or tissue paper).
- Clean the lower surface of the eye piece (inside the microscope tube) with a fine paintbrush.
- Cleaning the condenser and mirror.
- The condenser is cleaned with a soft cloth moistened with xylene.
- The mirror is cleaned with a soft cloth moistened with alcohol.
- Cleaning the support and the stage
- Clean with chamois leather or a soft piece of cloth (xylene should not be used, which may remove the black paint).
- The stage can be cleaned thoroughly well by using a piece of cloth impregnated with petroleum jelly.
What are types of microscopes?
7 types
Stereo Microscope.
Compound Microscope.
Inverted Microscope.
Metallurgical Microscope.
Polarizing Microscope.
fluorescence microscope
electron microscope
What is the main function of a compound microscope?
Typically, a compound microscope is used for viewing samples at high magnification (40 – 1000x), which is achieved by the combined effect of two sets of lenses: the ocular lens (in the eyepiece) and the objective lenses (close to the sample).